Thoracic osteochondrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic disease that affects the intervertebral discs; as the pathology progresses, the surrounding structures are involved in the process.Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis are varied, often similar to the manifestations of other diseases.To diagnose this pathology, a number of methods are used to detect changes in intervertebral structures.Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis includes both the use of medications and non-drug therapy in the form of physical therapy and massage.Many are also interested in how to cure thoracic osteochondrosis using traditional methods.
Risk factors
Thoracic osteochondrosis most often occurs if there are one or more predisposing factors.These include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- abnormalities of the spine;
- excessive physical activity;
- low physical activity;
- damage to the intervertebral discs after falls on the back, blows to the spine;
- prolonged exposure to vibration, which, for example, is typical for vehicle drivers;
- presence of excess body weight;
- hormonal disorders;
- smoking;
- age over 40 years;
- wearing high heels.
Features of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
Due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure, the thoracic spine is less mobile compared to the cervical spine, and it also bears less load compared to the lumbar part of the lumbar column.In this regard, osteochondrosis of this section rarely occurs.
The most common symptoms of osteochondrosis of the chest are dorsago, dorsalgia.Dorsago is a sharp pain that appears after a long stay in a lying position, sitting, when a person begins to stand up.Often the pain is so severe that breathing becomes difficult.This condition may be accompanied by muscle tension in the chest, neck, and lower back.
Dorsalgia is a gradually developing chest pain that persists for 2–3 weeks.Unpleasant sensations become stronger when bending, turning, staying in one position for a long time, or taking deep breaths.
Other common manifestations of thoracic osteochondrosis include:
- pain in the stomach, combined with nausea, vomiting, their occurrence is not associated with dietary habits;
- pain in the right hypochondrium, aggravated by coughing, sneezing, or changing body position;
- lower back pain, reminiscent of renal colic, they are sometimes accompanied by urinary disorders;
- pain in the upper chest, accompanied by a sensation of a foreign object in the throat;
- nagging pain in the mammary glands.
Degrees of the disease
Depending on the severity of the pathological process and manifestations of the disease, 4 degrees of osteochondrosis are distinguished.
First
At this stage, cracks form in the fibrous ring, into which the nucleus pulposus penetrates.Pain at the site of the lesion is a sign of osteochondrosis of the chest at this stage.They can be constant or appear suddenly, in the form of lumbago.Sometimes unpleasant sensations appear in the heart area, and local muscle contractions are noted.
Second
This stage is characterized by the occurrence of pathological mobility between the vertebrae at the site of the lesion.Pain occurs when staying in one position for a long time and persists with movement.
Third
This stage is characterized by rupture of the fibrous ring and the exit of the nucleus pulposus beyond its limits.Such pathological changes are accompanied by the formation of intervertebral hernias.The latter can compress nerve fibers, blood vessels, and the spinal cord.
Painful sensations occur more often and are accompanied by breathing problems and discomfort in the heart area.
Fourth
The pathological process involves the structures surrounding the intervertebral discs.The ligamentous apparatus of the spine is affected, andosteophytes- bone growths that compress nerve fibers, sometimes damaging the spinal cord.
Possible complications
When thoracic osteochondrosis is accompanied by compression of the spinal nerve root, intercostal neuralgia occurs.It is characterized by attacks of acute pain in one half of the chest.Unpleasant sensations spread from the spine to the sternum along the nerve fibers and are shooting in nature.
Pain with intercostal neuralgia often radiates to the stomach, shoulder blade, arm, and retrosternal region.When sympathetic fibers are damaged, paleness and redness of the skin in the affected area are noted.The duration of a painful attack is from several seconds to minutes.In the intercostal space, a person may experience paresthesia (a feeling of numbness, crawling), this symptom is characteristic of the time between attacks.
Another complication of this condition is spondyloarthrosis.With this pathology, the joints between the vertebrae are deformed, the cartilaginous layer is destroyed, the ligaments are stretched, and there is increased mobility of the vertebrae relative to each other.In response to inflammation, a spasm of the muscles surrounding the spine occurs.
Subsequently, osteophytes are formed, and against the background of the formation of such growths, the affected part of the spine loses mobility.Bone outgrowths sometimes compress the nerve roots, causing pain and sensory disturbances.
Diagnosis of the disease
The simplest way to detect thoracic osteochondrosis is radiography of the spine.This study reveals flattening, uneven contours of the intervertebral discs, displacement of the bodies of adjacent vertebrae in relation to each other, and changes in their shape.
Sometimes discography is performed - an X-ray examination using a contrast agent.This method allows us to identify the uneven boundaries of the nucleus pulposus, characteristic of osteochondrosis.With a pronounced pathological process, the contrast completely fills the intervertebral disc, sometimes extending beyond its limits.
More accurate images of the spinal column can be obtained using computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.These methods make it possible to assess in more detail the severity of the degenerative process, determine the presence of a hernia, its location, and size.
If symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis appear, the doctor may also recommend a general blood test as an auxiliary diagnostic method.This disease is often accompanied by a slight increase in the number of leukocytes and an increase in ESR.When testing blood for electrolytes, a decrease in calcium levels is sometimes noted.
Manifestations of thoracic osteochondrosis are similar to the signs of many diseases; if they occur, it is necessary to consult a doctor for examination and clarification of the diagnosis.If left untreated, the disease progresses, often leading to complications.
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis: gymnastics and exercise therapy
Gymnastics increases mobility in the intervertebral and costovertebral joints of the thoracic region, reduces the feeling of stiffness, and eliminates muscle spasm.
Before treating thoracic osteochondrosis at home with exercise therapy, you need to make sure there are no contraindications.Gymnastics classes are prohibited when:
- exacerbations of osteochondrosis;
- early recovery period after surgical treatment of osteochondrosis;
- neurological pathology accompanied by impaired coordination of movements;
- high blood pressure, heart rhythm disturbances;
- exacerbations of any chronic diseases, acute inflammatory and infectious processes.
Massage
Massage improves blood circulation in the tissues surrounding the spine, eliminates muscle spasm, while simultaneously increasing their tone.Against this background, pain and discomfort in the back area decrease.
For thoracic osteochondrosis, the following types of massage can be used:
- Classical.
- Point (impact on certain points).
- Segmental (back massage in the thoracic region, aimed at improving local blood circulation).
- Cupping (exposure to affected areas with vacuum).
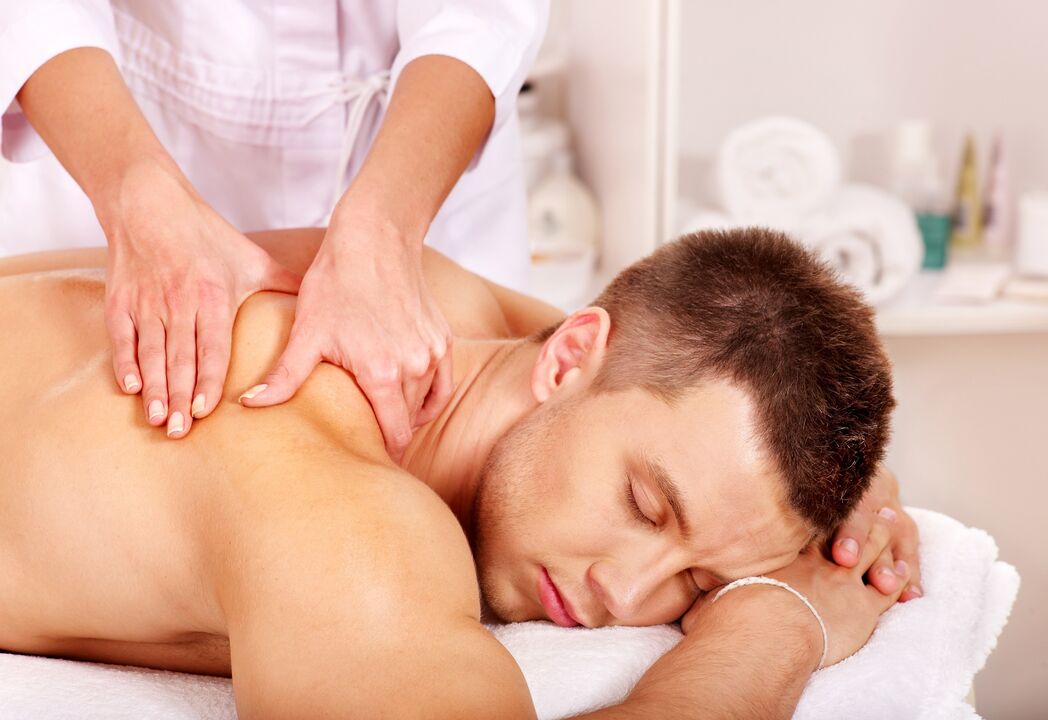

Classic massage includes rubbing, stroking, kneading, vibration movements, and pinching.
Drug treatment
Drug therapy for thoracic osteochondrosis is aimed at:
- reduction of inflammatory processes;
- elimination of pain;
- reduction of muscle spasm;
- improvement of the condition of cartilage and nervous tissue.
The most commonly used medications to treat the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.These drugs suppress inflammatory reactions that occur in nerve fibers, resulting in pain reduction.These funds are used in the form of:
- Tablets.
- Ointments, gels.
- Injections.
Injections of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used for exacerbations of the disease.
The most common side effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs include damage to the mucous membrane of the digestive tract with the formation of ulcers, decreased blood clotting, kidney damage, and allergic reactions.
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis with medications from the group of muscle relaxants can reduce spasm of the muscles surrounding the spine, compressing nerve endings and blood vessels, resulting in a decrease in the intensity of pain.
Chondroprotectors normalize metabolic processes in cartilage tissue and prevent its destruction.The composition of such products includes chondroitin sulfate, glucosamine, they take part in the synthesis of connective tissue.
Preparations containing B vitamins improve metabolism in damaged nerve fibers, which leads to the suppression of inflammatory reactions.
Folk remedies for the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis at home includes the use of ointments, compresses, and ingestion of various infusions and decoctions.They help reduce the severity of inflammation, improve metabolic processes in the affected areas of the spine, and reduce pain.
Ointments, compresses with natural composition
Before treating thoracic osteochondrosis with these medications, it is important to prepare them correctly.To obtain egg-vinegar ointment, you need to mix a chicken egg with the same volume of table vinegar, add 100 grams of soft butter to them, and bring the mixture to a homogeneous consistency.This ointment is applied to the affected area overnight in a thin layer.
To make another product, you need to mix 2 tablespoons of crushed sage and plantain leaves.Add 40 grams of melted Vaseline and 50 milliliters of olive oil to the plants.All components are thoroughly mixed, the resulting ointment is applied to the affected area with rubbing movements, and a warm cloth is applied on top.The procedure can be repeated 2-3 times a day.
To prepare one of the most effective compresses, you need to prepare 50 grams of aloe leaves, 100 milliliters of vodka, 100 grams of honey.Aloe is crushed using a grater, and the remaining ingredients are added.The composition is infused for 5 days.The product is applied to the area where pain is felt, polyethylene is placed on top of the skin of the back, and a towel or scarf is wrapped over the chest.The compress is left for 2 hours.
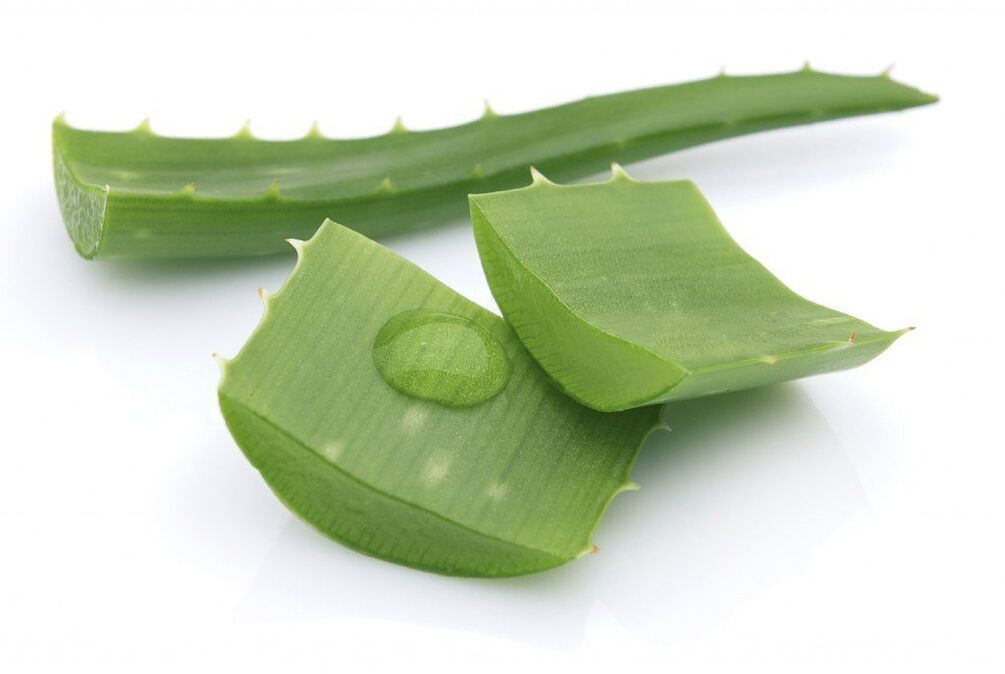

Infusions, tinctures, decoctions
To prepare an anti-inflammatory decoction, you need to mix a tablespoon of dried chamomile and mint.300 milliliters of hot water are added to the plant material, then the composition is boiled for 10 minutes using a water bath.The composition is taken 2 tablespoons three times a day.
To get an infusion with pronounced anti-inflammatory properties, you need to take 2 tablespoons of strawberry and birch leaves, 3 tablespoons of chamomile flowers, calendula, a tablespoon of St. John's wort, 10 grams of oak bark.The listed components are mixed, 2 tablespoons of this composition are poured with a liter of boiling water, and left for 4 hours.This infusion should be drunk 100 milliliters 3 times a day.
To obtain arnica tincture, 25 grams of plant flowers are poured with half a liter of vodka.The product is placed for a month in a dark, cool place.The tincture is taken 20 drops three times a day, after dissolving in a small amount of water.This remedy improves metabolic processes in the affected areas of the spine and reduces the severity of inflammatory reactions.
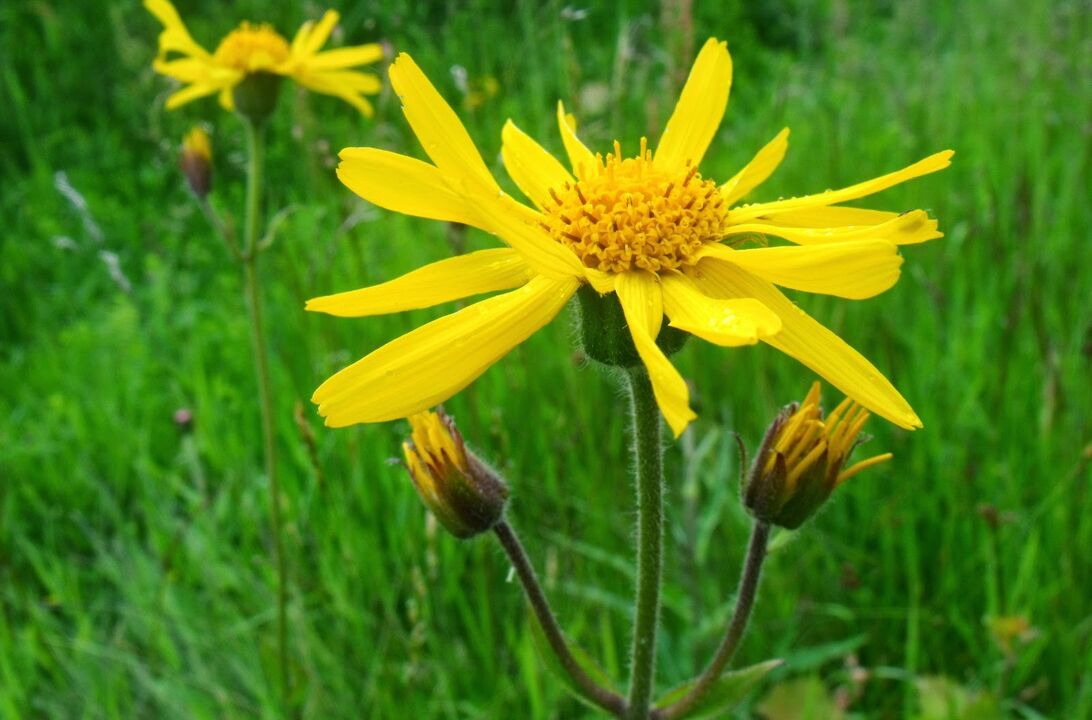

Prevention
To prevent the development of thoracic osteochondrosis, it is recommended:
- stop smoking and abusing alcoholic beverages;
- normalize nutrition, reduce the content of fatty, fried foods in the diet;
- maintain optimal body weight;
- Avoid heavy lifting and physical overexertion.
Complex treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis, consisting of drug therapy, massage, exercise therapy, is aimed at reducing inflammation, muscle spasms, and eliminating pain.Traditional methods serve as an auxiliary measure, helping to enhance the effect of other ongoing activities.